Waste Heat Extractor System
A heat pump transfers heat from one location to another rather than generating it. In heating mode, it extracts heat from the outside air, ground, or water and transfers it indoors. In cooling mode, the process is reversed, removing heat from inside and releasing it outdoors.
Traditional heating systems, such as those using combustion or electrical heating elements, convert energy from fuel or electricity into heat with typical coefficients of performance (COP) ranging between 0.85 and 0.95, meaning 5% to 15% of energy is lost during conversion. In contrast, heat pumps do not create heat but simply move it.
By utilizing a refrigerant that absorbs and releases heat as it circulates, heat pumps are 2 to 3 times more efficient, with a COP that can reach 3 to 4 depending on the design and operating conditions.
Industrial Applications of Heat Pumps
Waste Heat Recovery
Heat pumps capture waste heat from industrial process effluent such as hot exhaust gas or condensate return and reuse it for other process with heating requirements that typically heat exchangers cannot meet
Process Heating
Heat pumps provide precise temperature control in processes like food and beverage production, chemical manufacturing, and paper production
Drying Operations
In industries like textiles, food processing, and lumber, heat pumps can efficiently remove moisture from products by transferring heat during drying
District Heating
Large heat pumps can supply hot water and space heating to multiple buildings or an entire industrial complex.
Hot Water Production
Industrial facilities use heat pumps to generate hot water for cleaning in place(CIP) and sanitization
How Heat Extractor Technology Works
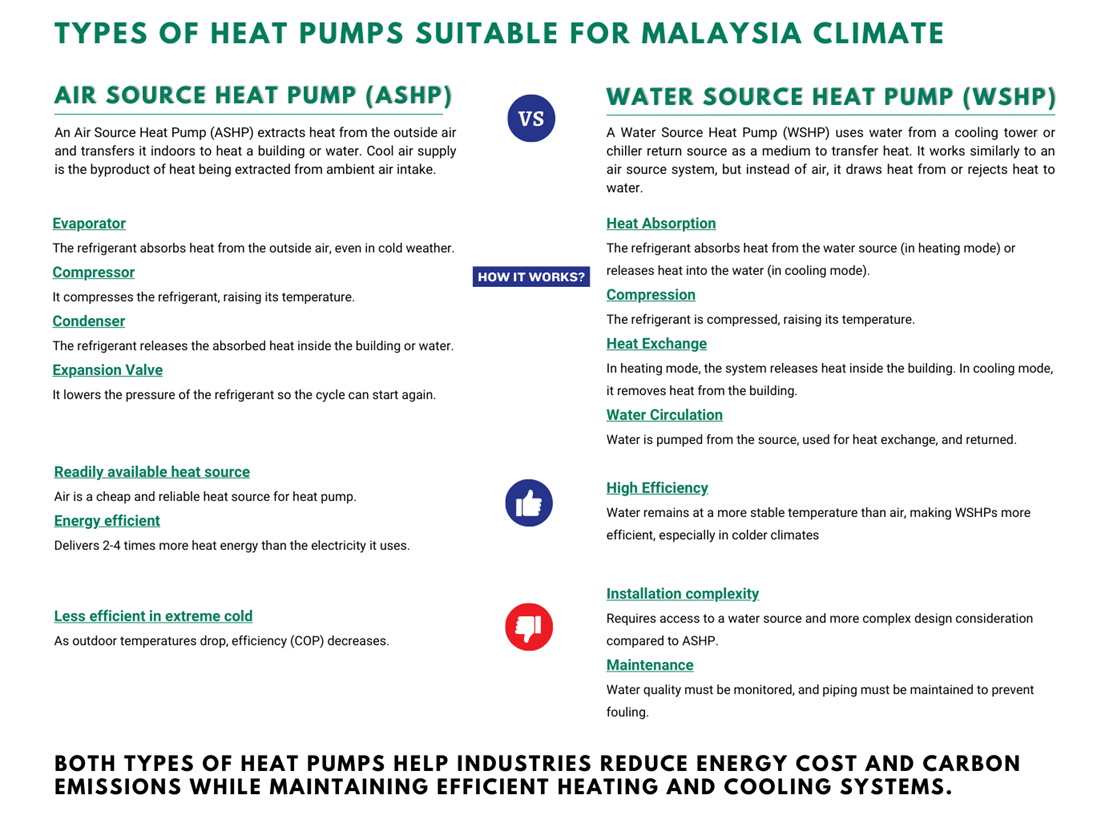
Types of heat pumps suitable for Malaysia climate can be categorised into two: Air Source Heat Pump (ASHP) and Water Source Heat Pump (WSHP). Here are how they work along with their pros and cons:
Related Content

Heat Recovery
Heat is generated as a byproduct in many industrial and commercial processes, often because of inefficiencies in energy use. Heat recovery is a process of capturing heat that would otherwise be wasted in various processes, then reusing it for other purposes, improving energy efficiency of systems and operational cost.

